1.2.4 - Captions (Live) - AA
Intent
Enable people who are deaf or hard of hearing to understand the auditory information in real-time synchronized media by providing captions.
All of the points from the 1.2.2 Captions (Prerecorded) - A apply to this criterion, except for open captions, as it is not likely the open captions will be present in the live media.
Real-time or Live media
Real-time (or live-streamed) media include live news broadcasts, live sport commentaries, live webinars, live event broadcasts, and similar.
Techniques
There are currently 3 techniques how to include the real-time captioning:
Communication Access Realtime Translation (CART)
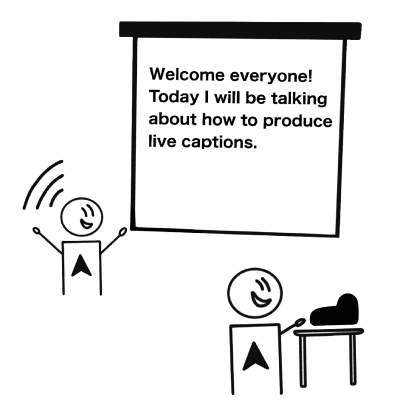
Also called real-time stenography - a system that stenographers and others use to convert speech to text. A highly skilled operator writes the exact words spoken using a special keyboard to produce live captions.
A stenographer is a person who makes a written verbatim record using a unique shortened writing style called "steno" on a steno machine.
Automated Voice Recognition Service Provided by a Shadow Speaker
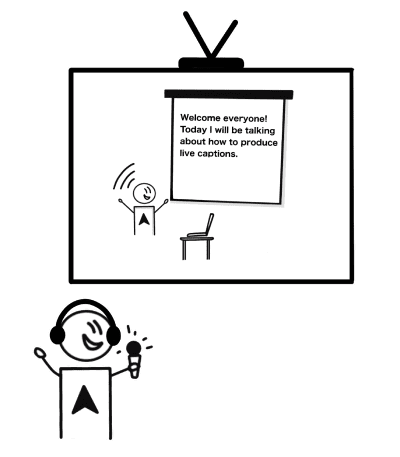
A highly skilled speaker repeats spoken content into a microphone and specialized voice recognition software (trained to a specific person's voice) interprets the speech as text and facilitates text correction and customization.
Automated Speech Recognition Software

An accurate software on a similar level as CART that automatically converts speech to text.
Examples
Correct Usage
The following example shows the correct usage or implementation of accessibility.
Example 1: CART
See a showcase of the Communication Access Realtime Translation (video).
Incorrect Usage
The following example shows incorrect usage or implementation of accessibility.
Example 1: No Live Captioning
Not including live captions in live news broadcasts, sports commentaries, or webinars is excluding people who cannot hear the audio track.
Test Your Knowledge
A stenographer repeats spoken content into a microphone so voice recognition software can interpret the speech as text. True or false?
False - a stenographer writes, whereas a shadow speaker speaks.
Synchronized media is audio or video content synchronized with another format for presenting information. True or false?
True - no catch here.